This article will provide you with a basic overview of type 2 diabetes and how to handle it. You’ll learn about the treatment options available, how to manage it, and what your long-term goals should be. Type 2 diabetes can be challenging and can be difficult to cope with. Luckily, there are a number of resources available to help you make the transition. If you’ve recently been diagnosed, follow these tips to make it as easy as possible.
About type 2 diabetes
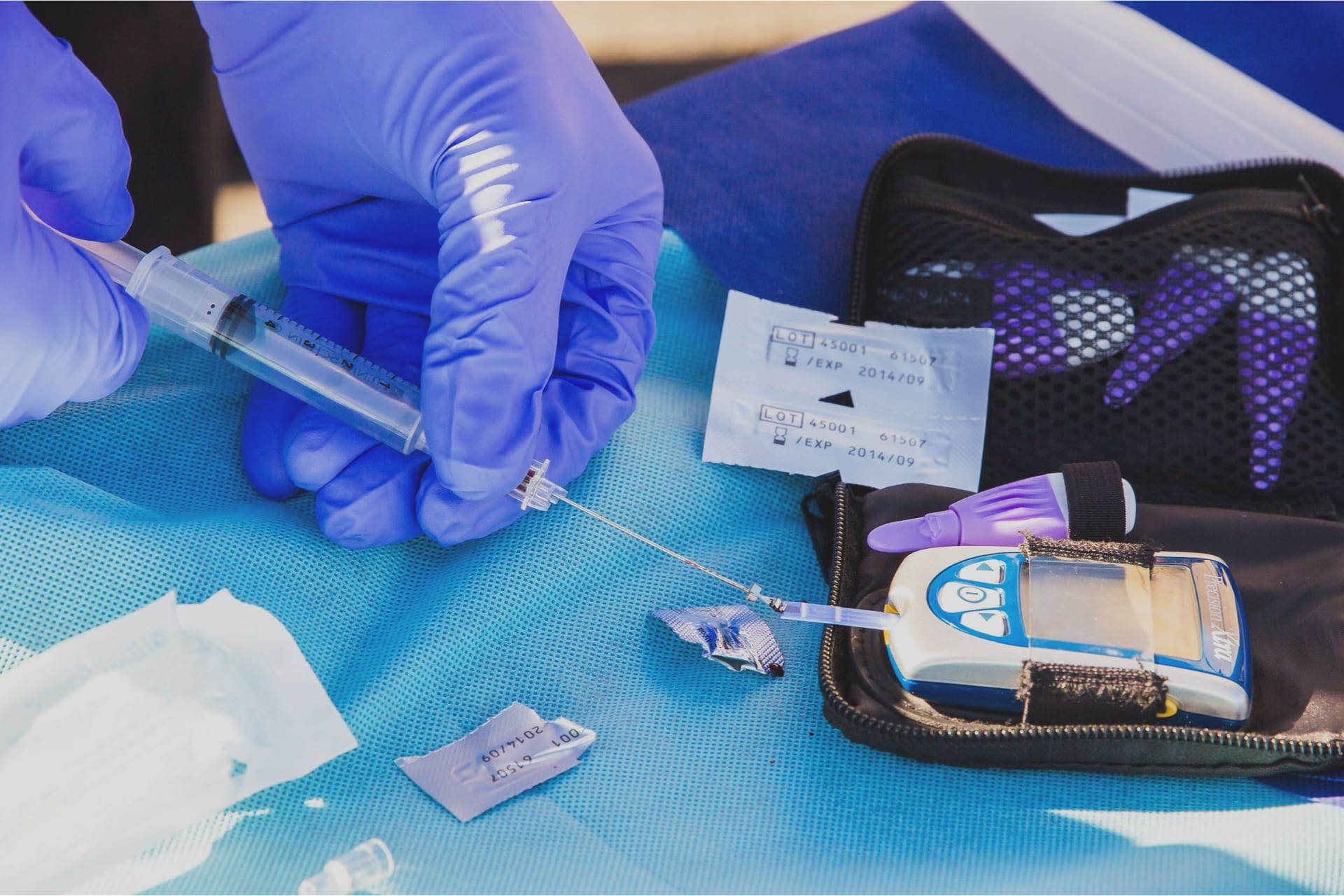
There are a few things you should know about type 2 diabetes. For starters, it’s important to keep your blood sugar levels regularly monitored. You should see your doctor for tests at least twice a year. If your blood sugar level is stable, the doctor might suggest two tests a year. If it’s unstable, more frequent tests are necessary. If you’re already diagnosed, you should start making healthy changes to your lifestyle and balancing your medications.
Type 2 diabetes is often referred to as adult-onset diabetes. It occurs when the body no longer produces or responds to insulin properly. As a result, it must use other sources of energy to function properly. This leads to a number of symptoms, some of which become more severe over time. If not treated promptly, this disease can lead to more serious complications. Without insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream and damages many organs and tissues.
High blood sugar is harmful for the brain. This is why people with diabetes have a slower healing time when their wounds become infected. Women with diabetes are more likely to experience miscarriage, stillbirth, and birth defects. People with diabetes are also more likely to develop hearing and sleep apnea, which are both common problems associated with diabetes. Diabetes is associated with increased risk for heart disease and stroke. It can also affect nerves in the limbs, leading to tingling, burning, and loss of feeling.
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes depends on your age and race. Type 2 diabetes tends to run in families. Being overweight or obese increases your risk. Some medicines can increase your risk, such as certain water pills, steroids, and antipsychotic drugs. You are also more likely to develop diabetes if you have African, Asian, Pacific Island, or American Indian heritage. So, as you can see, there’s a lot you can do to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
In addition to proper diet and exercise, you can also enroll in the National Diabetes Services Scheme. This program offers free resources, support, and subsidised diabetes products. It is administered by Diabetes Australia. Your doctor can refer you to a dietitian if you want more information about type 2 diabetes. You can optimise your blood sugar levels by eating foods with low glycemic index. Some of these foods include wholegrain breads, legumes, fruit, and minimally processed breakfast cereals.
Diagnosis
The prevalence of diabetes among people aged 45 to 64 years is about seven percent, and the rate rises to fifteen percent in certain minority groups. However, diabetes is largely undiagnosed, with an estimated 8 million Americans living with diabetes undiagnosed. Undiagnosed diabetes mellitus puts the patient at risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and other complications. Even if symptoms are not apparent, untreated diabetes puts the patient at high risk for developing complications such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, and obesity.
The early symptoms of type 2 diabetes are often vague and nonspecific. A blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL indicates diabetes. Patients with prediabetes do not have any symptoms but have blood sugar levels that range from 100 to 125 mg/dL. These people may also have symptoms of fatigue, frequent infections, and unexplained weight loss. Fortunately, lifestyle changes can help control the diabetes condition and its complications.
Blood glucose levels can be monitored using an HbA1c test. This test determines the average blood glucose level over the last three months. A high value means you have type 2 diabetes. Your doctor may perform the test during routine medical tests, which can be helpful in monitoring your condition. If your blood glucose level is too high or low, your doctor will need to order a blood test to determine whether or not you have the condition.
Unlike the symptoms of type 1 diabetes, the cause of type 2 diabetes is genetic. The patient must have certain traits or be born with it. There is no one genetic test that can determine the risk of developing the disease. Because of the wide genetic diversity, there are several causes for the disease. Some people respond well to simple lifestyle changes while others may require multiple types of medication. In any case, you must continue to follow your doctor’s instructions for good health.
Aside from causing serious health complications, diabetes can lead to other complications, including heart attacks and stroke. These complications can be fatal. If you do not take action to treat your diabetes, you may develop other health problems. While you can still control your blood glucose levels, you must also manage high blood pressure, cholesterol, and excess weight to maintain optimal health. In addition, diabetes can cause damage to your kidneys and retina, which can lead to eye complications.
Treatment
A new class of drugs is available for people with type 2 diabetes. These medications work to reduce blood sugar levels and remove glucose through the urine. This new class of drugs may have other benefits as well, including cardiovascular benefits and a slowing of the progression of chronic kidney disease. These drugs have several brand names, but they are often limited to obese people over the age of 35. Here are some of the most common types of type 2 diabetes medications.
Regular physical activity is good for everyone. Choose activities you enjoy and can fit into your lifestyle. These will make exercise easier to stick with. Always discuss your plans with your health care provider before starting a new exercise routine. They will be able to advise you on the type, amount, and intensity of exercises that will be most effective for you. These are important aspects of any type of diabetes treatment. The goal of type 2 diabetes treatment is to prevent complications and improve your health.
If you want to learn more about the latest treatments for diabetes, you should read up on professional-level articles. They are intended to help doctors stay informed about new medical research and treatment options. They are long, complex, and contain multiple references for further research. However, these articles are best for people who know a lot about medical terms and want to learn from the same materials as medical professionals. You can also find reliable health information from organizations such as the World Health Organization and the American Diabetes Association.
For some people, lifestyle changes are enough to control their diabetes. For others, however, medications are necessary to maintain a normal blood sugar level. Insulin may also be necessary, if you cannot produce enough insulin on your own. Lifestyle changes include eating a well-balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding stress, and quitting smoking. Your doctor will also be able to prescribe you a medication to help with your diabetes.
Long-term goals
In order to successfully manage your diabetes, you should set long-term goals. These goals should be attainable and realistic, as setting unattainable ones may lead to failure. When you are setting your goals, you should also discuss them with your family members, as this will ensure that you’re holding yourself accountable and remain motivated. For example, if you’re aiming to lose weight for your health or the health of your family, you should consider the lifestyle changes that you will need to make in order to reach your goal.
The best way to make these goals achievable is to use your imagination and imagine the positive feelings that come with the new healthy lifestyle. Try to picture yourself feeling great, even if you’re not feeling motivated. You’ll likely find that it’s not easy to imagine these feelings, so tie them to your short-term and long-term goals. However, remember that achieving your long-term goals may take a lot of effort, so make sure that you set attainable goals for yourself.
Your blood glucose levels are important, but your goals are more important than ever. By controlling your blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy body weight, you will decrease your risk of developing eye problems. Managing your weight is also important for your overall health, as diabetes will affect your hormone levels, your sleep patterns, and your stress levels. Make sure that you set long-term goals for yourself to stay healthy. They can be set for a week or a month, or even for a lifetime.
Your blood glucose levels will change over time, but they will be much more manageable if you start managing your diabetes in childhood. If you’re ready to get smart, it’s time to set glycemic goals and stay within them. Your doctor will help you determine what’s best for you and your situation. But remember to check your blood sugar levels regularly. This way, you’ll know if you’re on track and can start taking medication.